After studying Human Body Proportions, now we will learn about Anatomy of Head. It will include, ‘The Proportions, Shape and Composition of Skull’, ‘How to differentiate between male & female skull’, ‘Placement & Function of Facial muscles’ & ‘How to construct a Human face using standard proportions’.
My name is Lalit Adhikari and we are at LTY. Let’s begin!
Table of Contents
Skull
Skull is the most complex part of the entire human skeletal structure. It is a bony structure that supports the face and forms a protective cavity for the brain. It is comprised of many bones which are formed by intramembranous ossification and joined by sutures (fibrous joints).
It is the foundation of the head, formed by the Cranium (which consists of the Cranial roof and Cranial base) and the Facial Bones.
We use Face and Hands extensively for various kind of Expressions and Gestures. So, the Anatomy Study of Head which is Skull and Muscles, becomes a vital component of Figure Drawing.
Skull as Art Form and Content
Skulls carry a lot of Meaning & Symbolism which can help to improve the depth of an artwork. Giving a certain freedom to the audience to create their own interpretation of the artist’s expression.
The most common symbolic use of Skull is
- Representation of Death
- Mortality
- The unachievable nature of Mortality
We can often recognize buried fragments of a partially revealed Skull even though other bones might look like shards of stone. Our brain has a specific region for recognizing faces and it’s so attuned to finding faces that it can see faces in emoticons created using punctuation marks.

The human skull don’t always represent something morbid. Rather, it can also represent the Appreciation of Life. It could also mean transformation or transitioning form life into the next realm.
Mexicans favor this belief in their holiday, Dias de Los Muertos.
It can also represent vanity in Human’s life. For example: Charles Allan Gilbert’s All in Vanity.

It is a depiction of a woman gazing at her reflection in the mirror where the image and reflection is actually a Skull.
Related Topics:
Proportion of Skull
We, humans, are all unique in personality and physique. The contour of face and head varies among all of us but there will always be basics to the shape of human head.
Some important points to remember:
- The length of one eye is same as the distance between our eyes.
- The length of both our eyes is just about our face’s width.
- If you want accurate proportions, divide the face into 4 sections, a vertical line & a horizontal line both passing through the middle.
- The width of one eye is the same distance between the bottom of nose and eye.
| Proportion of Skull | Image |
|---|---|
| The Eye Sockets are halfway between the Head & Chin. | 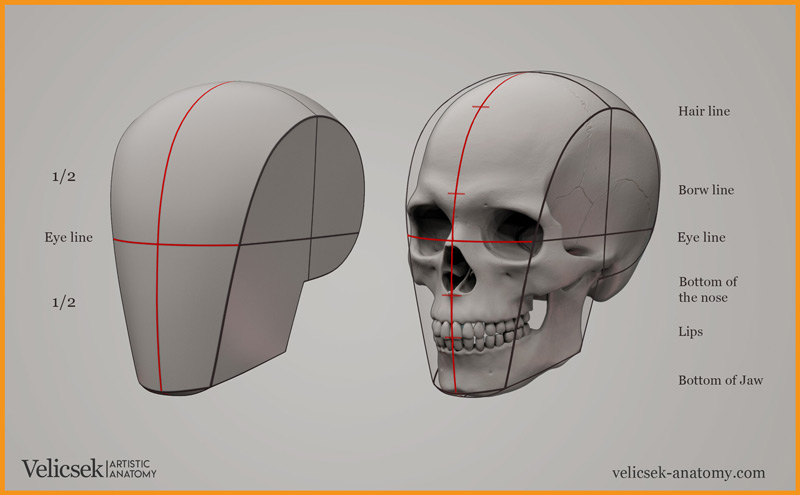 |
| The depth and height of Skull is similar. | 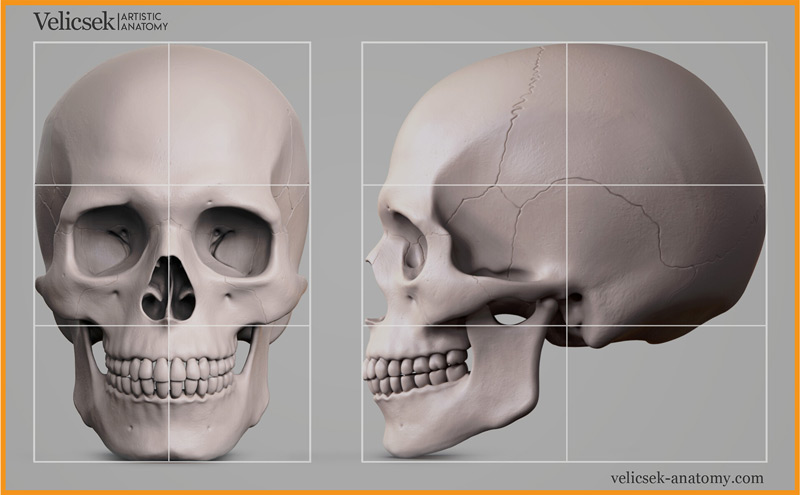 |
| The Facial muscles cover 1/3 of the head Cranial mass covers remaining 2/3 | 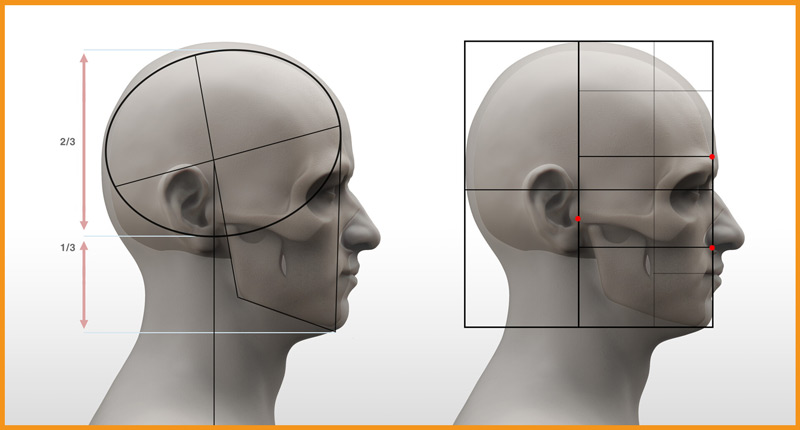 |
Bones of Skull

| Bones of Skull | Location |
|---|---|
| Frontal Bone | The Forehead structure that terminates at the brow. |
| Temporal Ridge | The Ridge that runs along the outer side of the upper Skull. It forms the square shape of the upper Head. |
| Parietal Bone | The bone along the side of the Head that forms a smooth curved surface. |
| Nasion | The point where the front of the Head meets the Nasal Bone. |
| Supraorbital Margin | The Ridge above the eyes. |
| Nasal Bone | The small bone at the top of the Nose. |
| Orbital Cavity | The Eye Well. |
| Infraorbital Margin | The lower Eye Ridge and the upper portion of the Cheek. |
| Zygomatic Bone | The Cheek Bone that lies under the Infraorbital Margin. |
| Maxilla | The upper Jaw Bone that lies under the Nose. |
| Mandible | The Bone that forms the lower Jaw. |
| Mental Protuberance | The tip of the Jaw Bone commonly known as the Chin. |
Difference between Male & Female Skull
The proportion varies for both – Male & Female Skull and it is essential to understand these differences.
| Parts of Skull | Male | Female |
|---|---|---|
| Cranial Mass | Massive & Deep | Rounder than male & Tapers at top |
| Supraorbital Margin | Round & appears dull | Sharper |
| Zygomatic Bone | Well-defined | Less pronounced |
| Mandible | Square-shaped | Round-shaped |
| Supercilary Arch | Large & Distinct | Smaller & Less pronounced |
Related Topics:
Facial Muscles
The Anatomy of Muscles in Face is related to Facial expressions. Movement of muscles in the Face changes the appearance and expressions. Hence, it is essential for artists to understand the arrangement of the muscles.
It is important to be familiar with the position, attachment and function of the muscles rather than just names. Some muscles are attached directly to the bones at both the ends while others are attached to bones at one end and with other band of muscles at the other end.
Muscles which are directly attached to the bones perform the function of moving the Bone Structure. Muscles that connects to other band of muscles at one end, perform the function of moving Flesh.
For Example: The most important muscle of the Head, is the muscle that closes the Jaw. It is place below & in-front of the ear. The Jaw is also attached to a muscle that spreads out over the sides of Cranium.
The Human Face, comprises of approximately 26 muscles. Out of these 26 muscles, only 10 muscles are responsible for the expressions.

| Muscle Name | Muscle Action |
|---|---|
| Masseter | Acts to raise the Jaw & Clenches the Teeth. It is associated with Angry or Aggressive states, Fear & Yawn. |
| Orbicularis oculi | It is the Squinting Muscle. Encircles the Eyes when it is closed, winking or tired. It is associated with closing Eyelids & compressing the eye opening. |
| Corrugator | It is the Frown Muscle. It compresses the skin between the eyebrows. It is associated with Frown, Concern & Concentration. |
| Frontalis | It is the Brow lifting muscle. It draws the Scalp down & depicts wrinkles on two sides. It is associated with Fear & Smile. |
| Levator labii | It is the Sneering Muscle. It raises the upper lip beneath the Nostrils. It is associated with Disgust & Disdain. |
| Zygomaticus major | It is the Smiling Muscle. It raises the mouth Upward & Outward. It is associated with Smiling & Laughing. |
| Risorius | It is the lower lip stretching muscle. It draws lower lip down & neck muscle outward. It is associated with crying & a state of shock or terror. |
| Triangularis | It is the Facial Shrug muscle. It pulls the corner of the mouth downward. It is associated with sadness, crying & unhappiness. |
| Depressor | It is lower lip curl muscle. It pulls the lower lip, down & out, around the lips. It is associated with expressing surprise. |
| Mentalis | It is the Pouting muscle. It raises & tightens chin. It is associated with sadness & fear. |
| Orbicularis oris | It is lip tightener muscle. It compresses & purses lips. It is associated with disdain & repulsion. |
Related Topics:
Proportions of Face
The proportions of each face vary but still there are some standards that we need to adhere as an artist.

- The eyes are halfway between the top of Head & Chin.
- Nose line is exactly distant from eye line by two eye units.
- Nose width is exactly one eye until wide.
- Mouth line is one eye unit from the Nose line.
- Top of ears line up above the eyes
- Bottom of ears line up with the bottom of nose.








